Abundance Frequency Count of a Community
AbdFreqCount.RdCounts the number of species observed the same number of times.
Usage
AbdFreqCount(Ns, Level = NULL, PCorrection="Chao2015", Unveiling="geom",
RCorrection="Rarefy", CheckArguments = TRUE)Arguments
- Ns
A numeric vector containing species abundances.
- Level
The level of interpolation or extrapolation. It may be an an arbitrary sample size (an integer) or a sample coverage (a number between 0 and 1).
- PCorrection
A string containing one of the possible corrections to estimate a probability distribution in
as.ProbaVector:"Chao2015"is the default value. Used only for extrapolation.- Unveiling
A string containing one of the possible unveiling methods to estimate the probabilities of the unobserved species in
as.ProbaVector:"geom"(geometric: the unobserved species distribution is geometric) is the default value. Used only for extrapolation.- RCorrection
A string containing a correction recognized by
Richnessto evaluate the total number of species inas.ProbaVector."Rarefy"is the default value to estimate the number of species such that the richness of the asymptotic distribution rarefied to the observed sample size equals the observed number of species in the data. Used only for extrapolation.- CheckArguments
Logical; if
TRUE, the function arguments are verified. Should be set toFALSEto save time when the arguments have been checked elsewhere.
Details
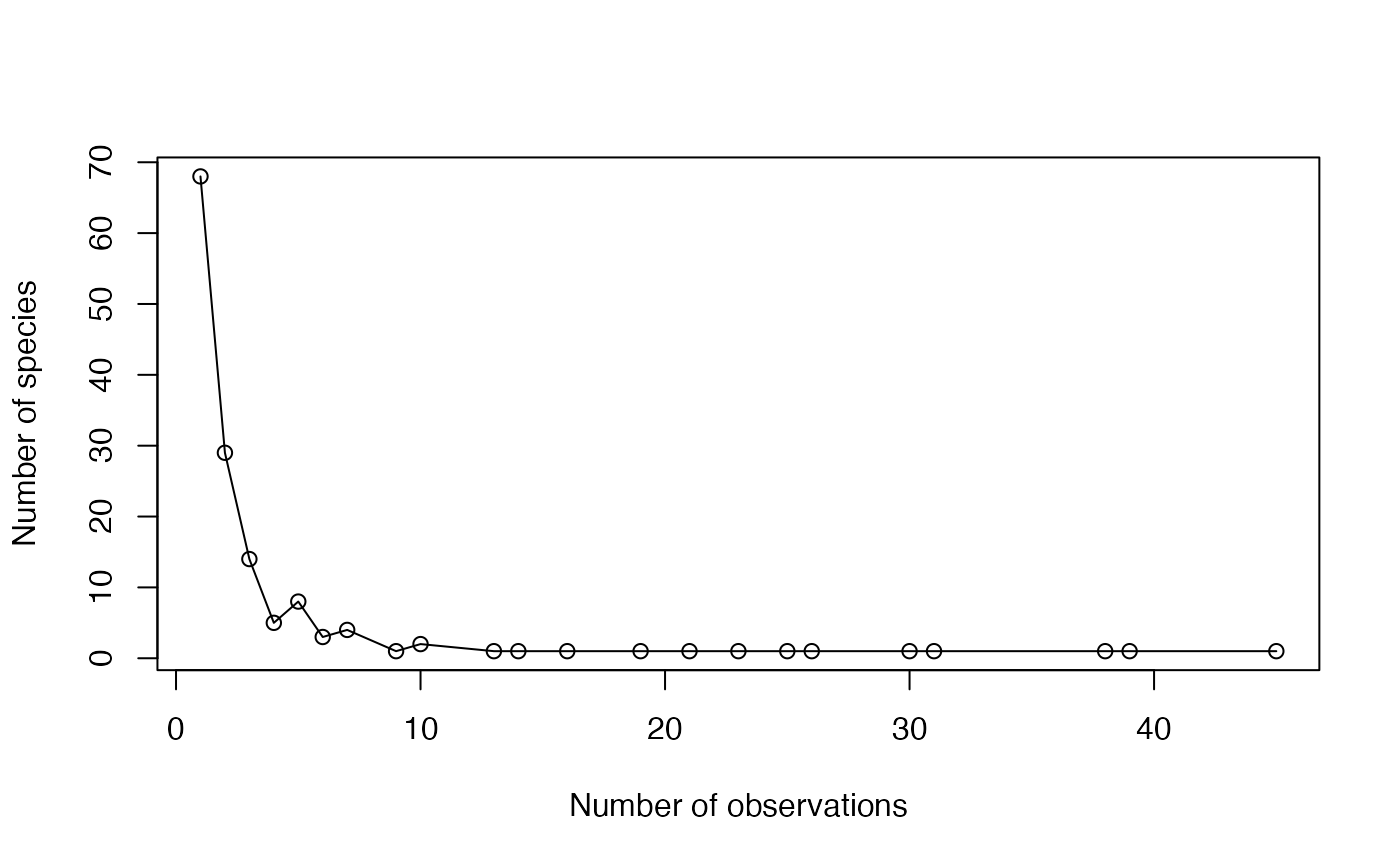
The Abundance Frequency Count (Chao et al., 2015) is the number of species observed each number of times.
It is a way to summarize the species distribution.
It can be estimated at a specified level of interpolation or extrapolation.
Extrapolation relies on the estimation of the estimation of the asymptotic distribution of the community by as.ProbaVector and eq. (5) of Chao et al. (2014).
Value
A two-column matrix. The first column contains the number of observations, the second one the number of species observed this number of times.
References
Chao, A., Gotelli, N. J., Hsieh, T. C., Sander, E. L., Ma, K. H., Colwell, R. K., Ellison, A. M (2014). Rarefaction and extrapolation with Hill numbers: A framework for sampling and estimation in species diversity studies. Ecological Monographs, 84(1): 45-67.
Chao, A., Hsieh, T. C., Chazdon, R. L., Colwell, R. K., Gotelli, N. J. (2015) Unveiling the Species-Rank Abundance Distribution by Generalizing Good-Turing Sample Coverage Theory. Ecology 96(5): 1189-1201.
Examples
# Load Paracou data (number of trees per species in two 1-ha plot of a tropical forest
# and their taxonomy)
data(Paracou618)
# Ns is the vector of abundances of the first plot
Ns <- Paracou618.MC$Nsi[, 1]
# Return the abundance frequency count
(AbdFreqCount(Ns) -> afc)
#> Abundance NbSpecies
#> [1,] 1 68
#> [2,] 2 29
#> [3,] 3 14
#> [4,] 4 5
#> [5,] 5 8
#> [6,] 6 3
#> [7,] 7 4
#> [8,] 9 1
#> [9,] 10 2
#> [10,] 13 1
#> [11,] 14 1
#> [12,] 16 1
#> [13,] 19 1
#> [14,] 21 1
#> [15,] 23 1
#> [16,] 25 1
#> [17,] 26 1
#> [18,] 30 1
#> [19,] 31 1
#> [20,] 38 1
#> [21,] 39 1
#> [22,] 45 1
#> attr(,"class")
#> [1] "AbdFreqCount" "matrix" "array"
plot(afc, xlab="Number of observations", ylab="Number of species")
lines(afc)