Simulations of a point pattern according to the null hypothesis of population independence defined for M
rPopulationIndependenceM.RdSimulates of a point pattern according to the null hypothesis of population independence defined for M
Arguments
- X
A weighted, marked, planar point pattern (
wmppp.object).- ReferenceType
One of the point types.
- CheckArguments
Logical; if
TRUE, the function arguments are verified. Should be set toFALSEto save time in simulations for example, when the arguments have been checked elsewhere.
Details
Reference points are kept unchanged, other points are redistributed randomly across locations.
Value
A new weighted, marked, planar point pattern (an object of class wmppp, see wmppp.object).
References
Marcon, E. and Puech, F. (2010). Measures of the Geographic Concentration of Industries: Improving Distance-Based Methods. Journal of Economic Geography 10(5): 745-762.
Marcon, E., F. Puech and S. Traissac (2012). Characterizing the relative spatial structure of point patterns. International Journal of Ecology 2012(Article ID 619281): 11.
Examples
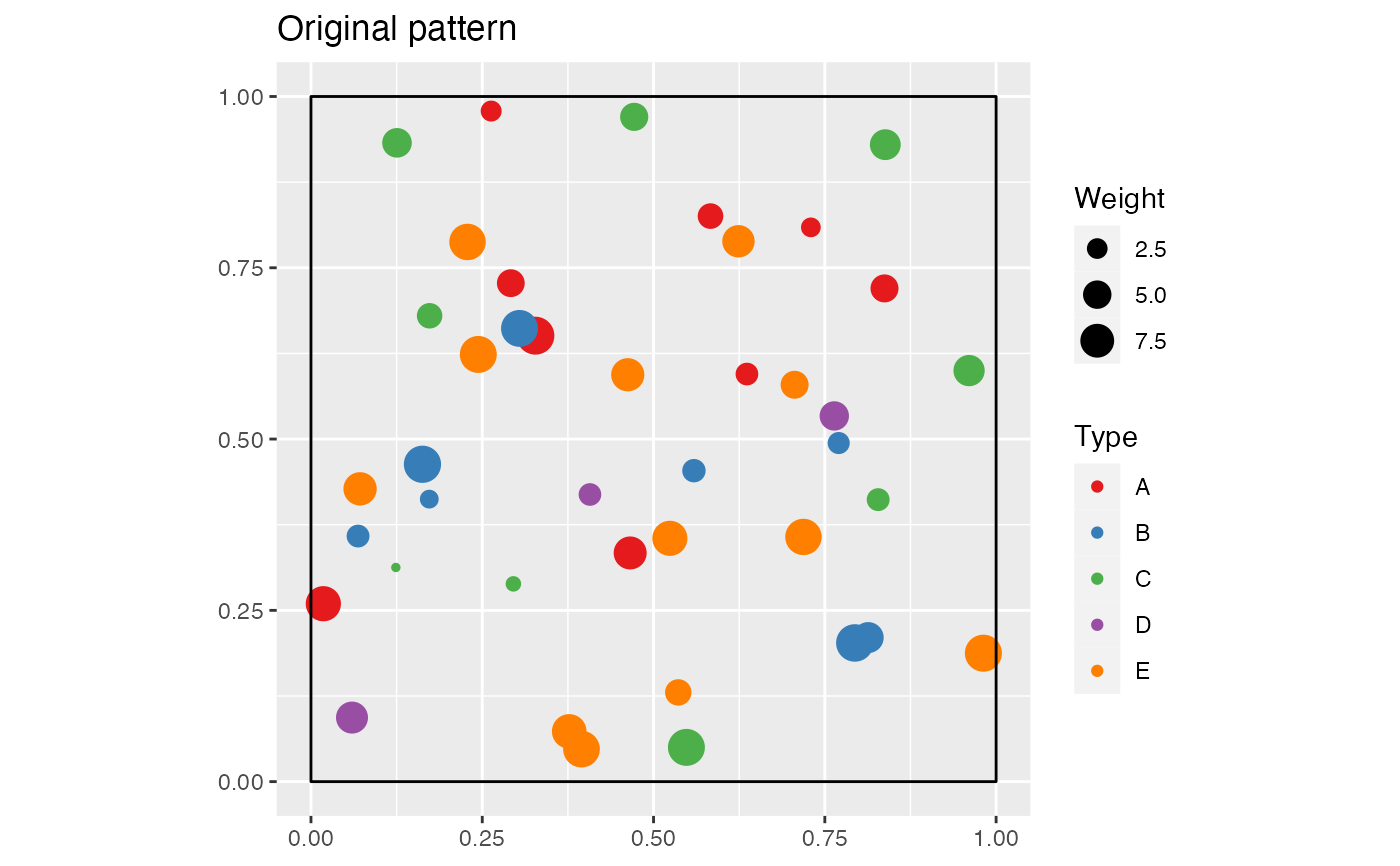
# Simulate a point pattern with five types
X <- rpoispp(50)
PointType <- sample(c("A", "B", "C", "D", "E"), X$n, replace=TRUE)
PointWeight <- runif(X$n, min=1, max=10)
marks(X) <- data.frame(PointType, PointWeight)
X <- as.wmppp(X)
autoplot(X, main="Original pattern")
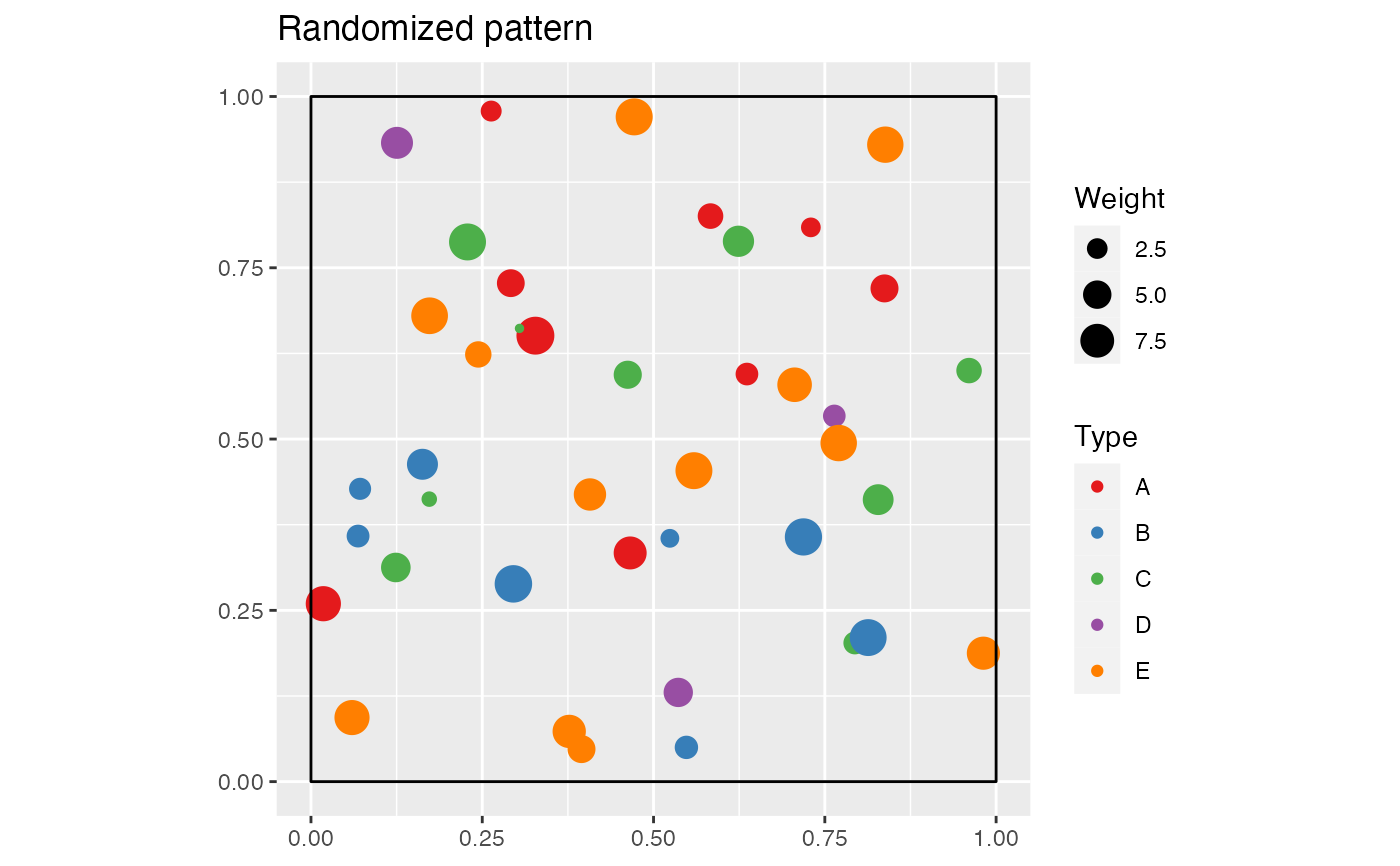
 # Randomize it
Y <- rPopulationIndependenceM(X, "A")
# Points of type "A" are unchanged,
# all other points have been redistributed randomly across locations
autoplot(Y, main="Randomized pattern")
# Randomize it
Y <- rPopulationIndependenceM(X, "A")
# Points of type "A" are unchanged,
# all other points have been redistributed randomly across locations
autoplot(Y, main="Randomized pattern")