Apply a Function over a Phylogenetic Tree
PhyloApply.RdCuts the tree into slices separated by nodes, applies the function to each slice and returns the weighted (by slice lengths) sum of the results.
Arguments
- Tree
An object of class
hclust, "phylo" (seeread.tree),phylogorPPtree. The tree must be ultrametric.- FUN
The function to be applied to each interval of the tree.
- NorP
A numeric vector or a two-column matrix. Contains either abundances or probabilities. Two-column matrices should contain the observed abundances (or probabilities) in the first column and the expected ones in the second column, to allow using beta diversity functions.
- Normalize
If
TRUE(default), theTotalvalue returned byFunctionis normalized by the height of the tree (it is the weighted average value of the result in each slice).
IfFALSE, it is the unnormalized weighted sum of the results.- dfArgs
A dataframe. Columns are arguments for
FUN: their names are those of valid arguments. Values will be passed toFUNin each slice of the tree, starting from the tips. The number of lines must equal the number of slices.- ...
Further arguments to pass to
Function.- CheckArguments
Logical; if
TRUE, the function arguments are verified. Should be set toFALSEto save time when the arguments have been checked elsewhere.
Details
This funtion is generally not used directly. It is a tool to calculate PhyloEntropy and PhyloDiversity.
Intervals (slices) separate two cuts (nodes) in a tree: no node is found at heights contained in an interval.
Objects of class PPtree are returned by Preprocess.Tree.
... allow passing arguments to the function but they can't change along the tree. If necessary, dfArgs allow passing a different value for each slice of the tree.
Value
An object of class PhyloValue. It is a list:
- Distribution
The distribution used to calculate the value
- Function
The function used to calculate the value
- Tree
The functional or phylogenetic tree used to calculate the value
- Normalized
Logical. Indicates whether phylovalue is normalized or proportional to the height of the tree.
- Cuts
A named vector containing values along the tree. Names are cut ends, i.e. the ends of intervals (the first interval starts at 0 for leaves, the max value is the height of the tree).
- Corrections
A named vector containing the correction used by FUN to obtain each value of
Cuts. Names are those ofCuts.- Total
The total value, multiplied by the tree height if
Normalizeis FALSE.
References
Marcon, E., Herault, B. (2015). Decomposing Phylodiversity. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 6(3): 333-339.
Examples
# Load Paracou data (number of trees per species in two 1-ha plot of a tropical forest
# and their taxonomy)
data(Paracou618)
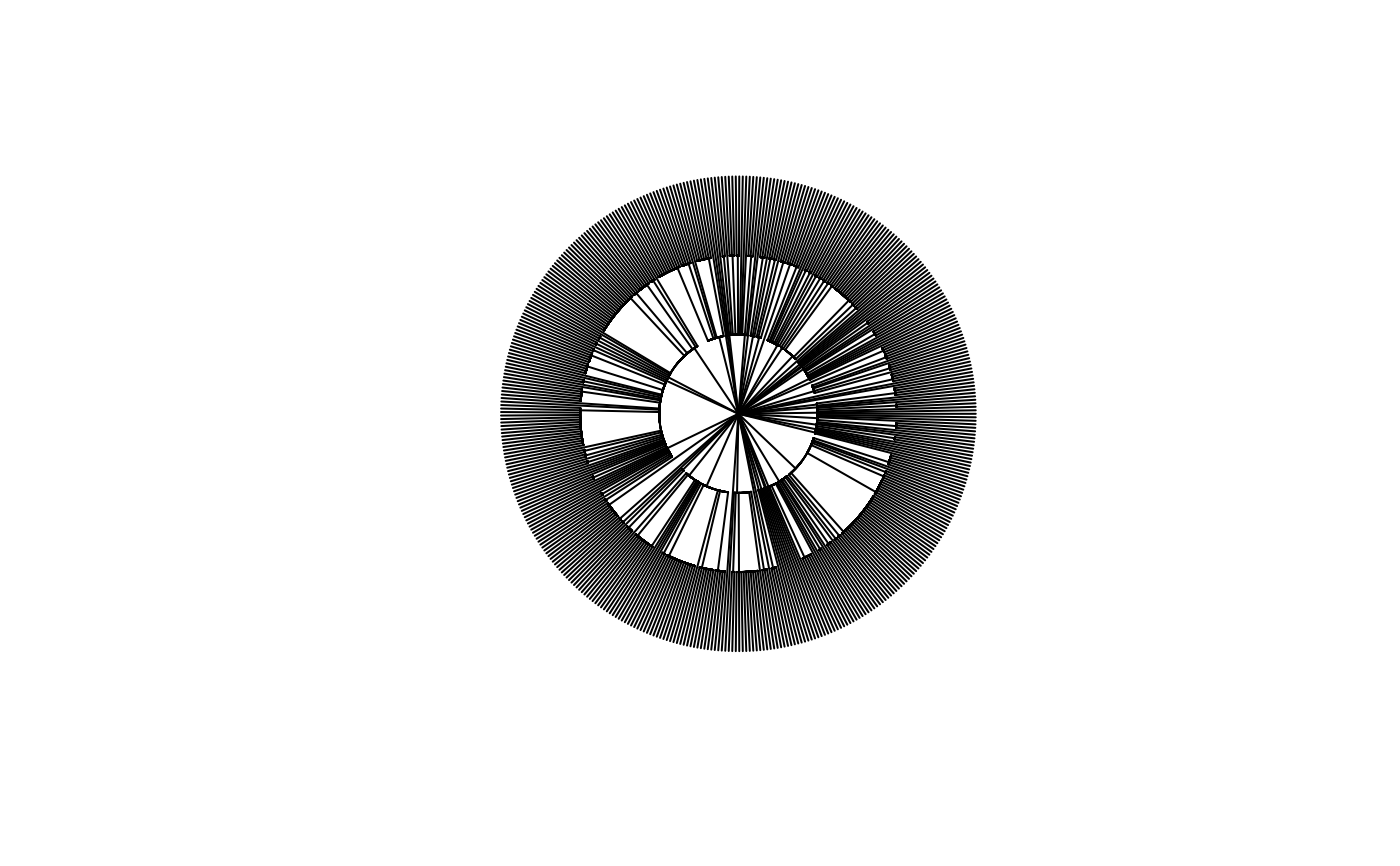
# Plot the taxonomy
plot(Paracou618.Taxonomy, type="fan", show.tip.label=FALSE)
 # Calculate the mean number of trees (individuals) per species
# (Cuts are 1=species, 2=genus, 3=family)
summary(PhyloApply(Paracou618.Taxonomy, mean, Paracou618.MC$Ns, TRUE))
#> mean applied to Paracou618.MC$Ns along the tree: Paracou618.Taxonomy
#>
#> Results are normalized
#>
#> The average value is: 10.26421
#>
#> Values along the tree are:
#> 1 2 3
#> 2.644706 6.108696 22.039216
# Calculate the mean number of trees (individuals) per species
# (Cuts are 1=species, 2=genus, 3=family)
summary(PhyloApply(Paracou618.Taxonomy, mean, Paracou618.MC$Ns, TRUE))
#> mean applied to Paracou618.MC$Ns along the tree: Paracou618.Taxonomy
#>
#> Results are normalized
#>
#> The average value is: 10.26421
#>
#> Values along the tree are:
#> 1 2 3
#> 2.644706 6.108696 22.039216