Bibliométrie avec R
Tutoriel pour la bibliométrie avec les données de Google Scholar ou de Scopus.
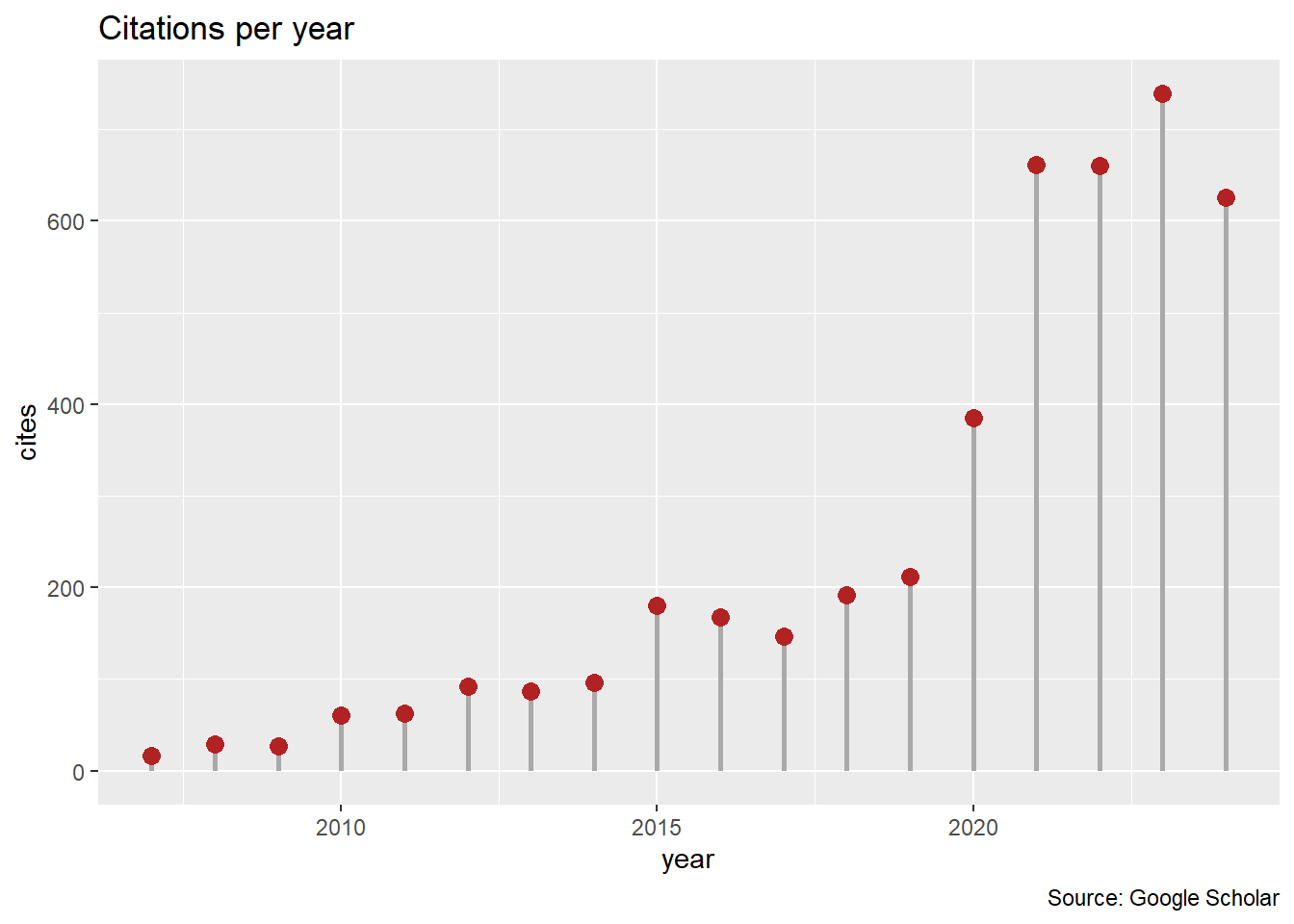
Le package scholar permet d’accéder à l’API de Google Scholar pour analyser la production d’un auteur (ou d’une structure) disposant d’un identifiant, donc d’une page, Google Scholar. Par exemple, les citations annuelles sont obtenues facilement:
library("scholar")
library("tidyverse")## ── Attaching core tidyverse packages ─────────────
## ✔ dplyr 1.1.4 ✔ readr 2.1.6
## ✔ forcats 1.0.1 ✔ stringr 1.6.0
## ✔ ggplot2 4.0.1 ✔ tibble 3.3.1
## ✔ lubridate 1.9.4 ✔ tidyr 1.3.2
## ✔ purrr 1.2.1
## ── Conflicts ──────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
## ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
## ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
## ℹ Use the conflicted package (<http://conflicted.r-lib.org/>) to force all conflicts to become errors"4iLBmbUAAAAJ" %>% # Eric Marcon
get_citation_history() %>% # Google Scholar API
ggplot(aes(year, cites)) +
geom_segment(aes(xend = year, yend = 0), linewidth = 1, color = 'darkgrey') +
geom_point(size = 3, color = 'firebrick') +
labs(
title = "Citations per year",
caption = "Source: Google Scholar"
)
A partir d’un export au format Bibtex d’une bibliographie obtenue avec Scopus, le package bibliometrix permet de nombreuses analyses.
Suivre les liens pour accéder au tutoriel complet: