Hurlbert's Index and Explicit Diversity
Hurlbert.RdCalculates the Hurlbert entropy of order \(k\) of a probability or abundance vector, and its effective number of species.
Usage
Hurlbert(NorP, k = 2, ...)
bcHurlbert(Ns, k = 2, CheckArguments = TRUE)
# S3 method for class 'ProbaVector'
Hurlbert(NorP, k = 2, ...,
CheckArguments = TRUE, Ps = NULL)
# S3 method for class 'AbdVector'
Hurlbert(NorP, k = 2, ...,
CheckArguments = TRUE, Ns = NULL)
# S3 method for class 'integer'
Hurlbert(NorP, k = 2, ...,
CheckArguments = TRUE, Ns = NULL)
# S3 method for class 'numeric'
Hurlbert(NorP, k = 2, ...,
CheckArguments = TRUE, Ps = NULL, Ns = NULL)
HurlbertD(NorP, k = 2, ...)
bcHurlbertD(Ns, k = 2, CheckArguments = TRUE)
# S3 method for class 'ProbaVector'
HurlbertD(NorP, k = 2, ...,
CheckArguments = TRUE, Ps = NULL)
# S3 method for class 'AbdVector'
HurlbertD(NorP, k = 2, ...,
CheckArguments = TRUE, Ns = NULL)
# S3 method for class 'integer'
HurlbertD(NorP, k = 2, ...,
CheckArguments = TRUE, Ns = NULL)
# S3 method for class 'numeric'
HurlbertD(NorP, k = 2, ...,
CheckArguments = TRUE, Ps = NULL, Ns = NULL)Arguments
- Ps
A probability vector, summing to 1.
- Ns
A numeric vector containing species abundances.
- NorP
A numeric vector, an integer vector, an abundance vector (
AbdVector) or a probability vector (ProbaVector). Contains either abundances or probabilities.- k
A number: the order of diversity. Default is 2 for Simpson's diversity.
- ...
Additional arguments. Unused.
- CheckArguments
Logical; if
TRUE, the function arguments are verified. Should be set toFALSEto save time when the arguments have been checked elsewhere.
Details
Hurlbert's index of diversity (1971) of order \(k\) is the expected number of species in a sample of size \(k\).
Bias correction requires the number of individuals. Use bcHurlbert. It is limited to orders \(k\) less than or equal to the number of individuals in the community.
The effective number of species HurlbertD (explicit diversity) has been derived by Dauby & Hardy (2012). It is calculated numerically. bcHurlbertD calculates it from the bias-corrected index bcHurlbert.
The functions are designed to be used as simply as possible. Hurlbert is a generic method. If its first argument is an abundance vector, an integer vector or a numeric vector which does not sum to 1, the bias corrected function bcHurlbert is called. Explicit calls to bcHurlbert (with bias correction) or to Hurlbert.ProbaVector (without correction) are possible to avoid ambiguity. The .integer and .numeric methods accept Ps or Ns arguments instead of NorP for backward compatibility.
Value
A named number equal to the calculated index or diversity. The name is either "Biased" or "Unbiased", depending on the estimator used.
References
Dauby G. & Hardy O.J. (2012) Sampled-based estimation of diversity sensu stricto by transforming Hurlbert diversities into effective number of species. Ecography 35(7): 661-672.
Hurlbert (1971) The Nonconcept of Species Diversity: A Critique and Alternative Parameters. Ecology 52(4): 577-586.
Examples
# Load Paracou data (number of trees per species in two 1-ha plot of a tropical forest)
data(Paracou618)
# Ns is the total number of trees per species
Ns <- as.AbdVector(Paracou618.MC$Ns)
# Species probabilities
Ps <- as.ProbaVector(Paracou618.MC$Ns)
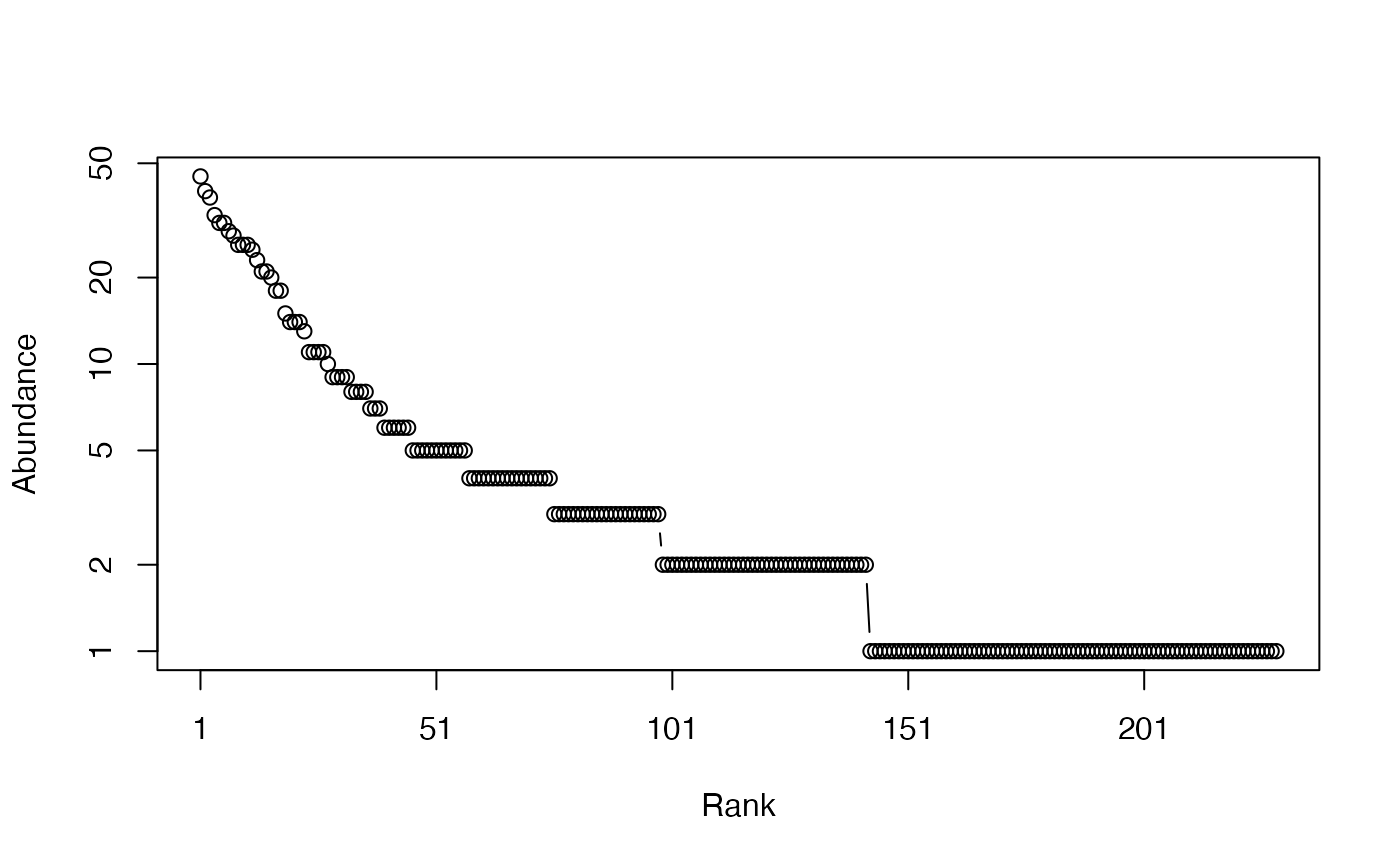
# Whittaker plot
plot(Ns)
 # Calculate Hurlbert entropy of order 2, equal to Simpson's index of diversity
Hurlbert(Ps, 2)
#> Biased
#> 1.985449
# Calculate an unbiased estimator of Hurlbert entropy of order 2
Hurlbert(Ns, 2)
#> Unbiased
#> 1.986326
# Calculate Hurlbert entropy of order 2, equal to Simpson's index of diversity
Hurlbert(Ps, 2)
#> Biased
#> 1.985449
# Calculate an unbiased estimator of Hurlbert entropy of order 2
Hurlbert(Ns, 2)
#> Unbiased
#> 1.986326